Lattice Addition Algorithm
Some of the worksheets for this concept are Name 2 digit by 2 digit lattice lattice multiplication Lattice multiplication Name 3 digit by 3 digit lattice lattice multiplication Lattice multiplication Left to right subtraction algorithm lattice algorithm for The lattice method of multiplication 1 teaching the lesson. Lattice Algorithm We explore this algorithm by looking at an example such as the one given in Figure 123.
 Lattice Method Multiplication Youtube
Lattice Method Multiplication Youtube
We model the algorithm with using base ten drawing to understand the importance of alignment in the algorithm.

Lattice addition algorithm. Lattice multiplication also known as the Italian method Chinese method Chinese lattice gelosia multiplication sieve multiplication shabakh diagonally or Venetian squares is a method of multiplication that uses a lattice to multiply two multi-digit numbers. Use the lattice algorithm to perform each of the following. Stack the numbers youre adding in a column keeping all of the digits in the right places you know the 1s digits in the 1s place 10s digits in the 10s place and so on.
Next multiply each number in the row by each number in the column. Students will be better equipped to tackle larger more complex addition problems and gain the confidence to attempt larger problems. Lattice Algorithm for Addition Overview.
Multiply 3 by 4 to get 12 and put 12 in intersection of the first row and the first column as show below. Notice that 3 is located in the first row and 4 in the first column. That is why the answer goes in the intersection.
Next we explore a couple of algorithms that have been used throughout his-tory. Lattice multiplication is also known as Italian multiplication Gelosia multiplication sieve multiplication shabakh Venetian squares or the Hindu lattice1 It uses a grid with diagonal lines to help the student break up a multiplication problem into smaller steps. By the same token multiply 5 and 2 and put the answer in the intersection of second row and the second column.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. For example say we. The multiplicand is the first number in a multiplication operation while the multiplier is the last number.
Introduction to Addition Addition Properties and Algorithms Mental Addition Algorithms Conclusion Addition Algorithms The Lattice Method The lattice method is similar to the standard method but no carrying is done. Draw a table with a x b number of columns and rows respectively. Lattice Addition Algorithm In the lattice algorithm for addition columns are added from.
Organize the places of the digits allowing the sums to be calculated with fewer carry operations provide an opportunity for. For simplification of the method adding or combining large numbers with different place values by using blinders will be incorporated. This section provides examples that demonstrate how to use a variety of algorithms included in Everyday MathematicsIt also includes the research basis and explanations of and information and advice about basic facts and algorithm development.
Instead the sum is found using a two-step process. In addition to drawing our boxes draw your lattice by starting from the upper right hand corner of each box and drawing diagonally down to the bottom left hand corner of the box. It is mathematically identical to the more commonly used long multiplication algorithm but it breaks the process into smaller steps which some.
This section provides examples that demonstrate how to use a variety of algorithms included in Everyday MathematicsIt also includes the research basis and explanations of and information and advice about basic facts and algorithm development. Figure 123 To use this algorithm you add single digit number to a single digit number from right to left and record the results in a lattice as shown. Lattice Addition - Displaying top 8 worksheets found for this concept.
Im going to do a couple of lattice multiplication examples in this video and the next one will try to understand why it worked so lets say were trying to multiply 27 times 48 what you do is you write down your 27 the 2 and the 7 are gonna get separate columns and you multi-multi your 48 down the right-hand side and then you draw a lattice this is why its called lattice multiplication so. Lattice Algorithm for Addition will be introduced in this lesson. The lattice method of addition uses the boxes and diagonals to _____.
The Lattice Algorithm can make large adding numbers seem less daunting and help to eliminate place value errors. The number a corresponds to the number of digits of the multiplicand number being multiplied and b to the digits of the multiplier number doing the multiplying. The addition lattice method is a means to perform simple addition of numbers in any base without explicitly carrying over digits from one column to another.
 What Is Lattice Multiplication Knilt
What Is Lattice Multiplication Knilt
 Lattice Multiplication Method Maths With Mum
Lattice Multiplication Method Maths With Mum
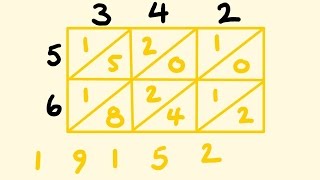 Lattice Multiplication Youtube
Lattice Multiplication Youtube
 Lattice Multiplication Method Maths With Mum
Lattice Multiplication Method Maths With Mum
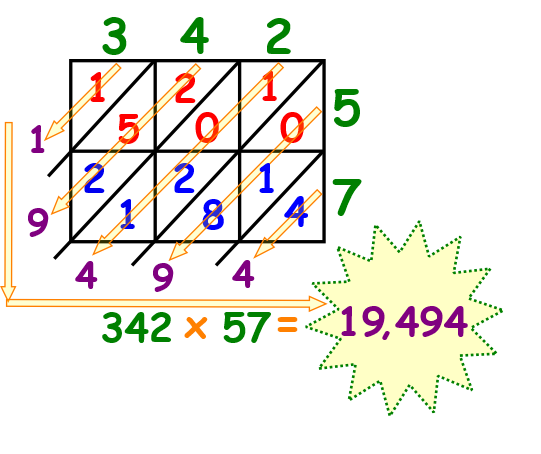 Lattice Multiplication Template Free Pdf To Practice Lattice Method
Lattice Multiplication Template Free Pdf To Practice Lattice Method
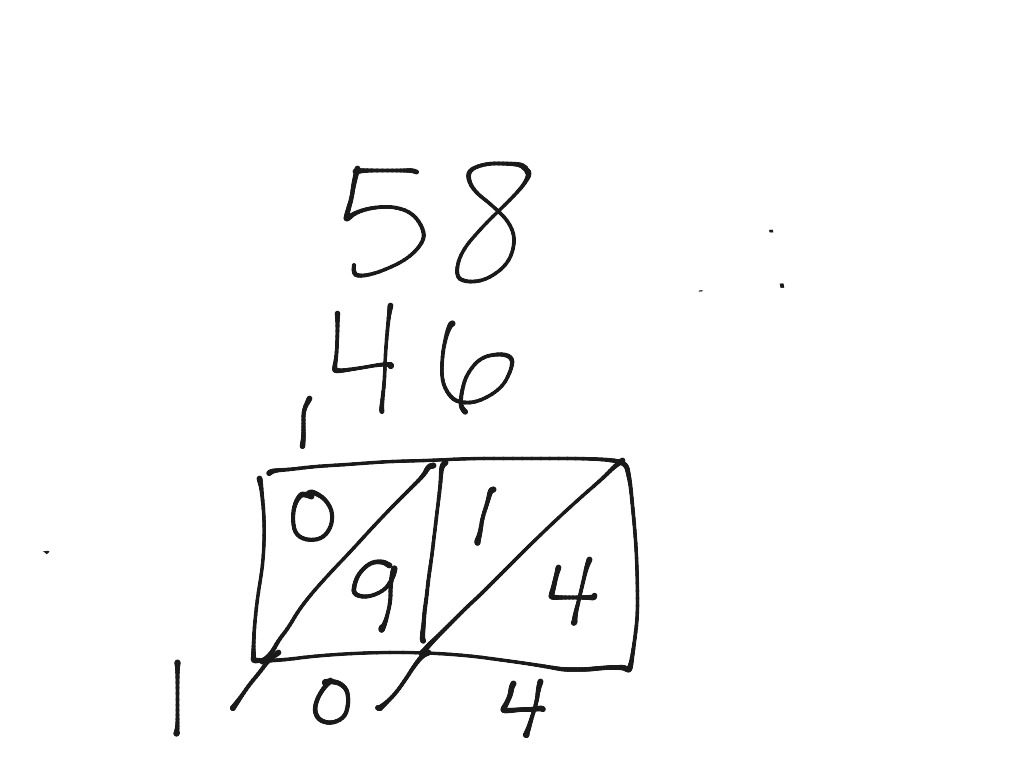 Lattice Method Addition Math Showme
Lattice Method Addition Math Showme
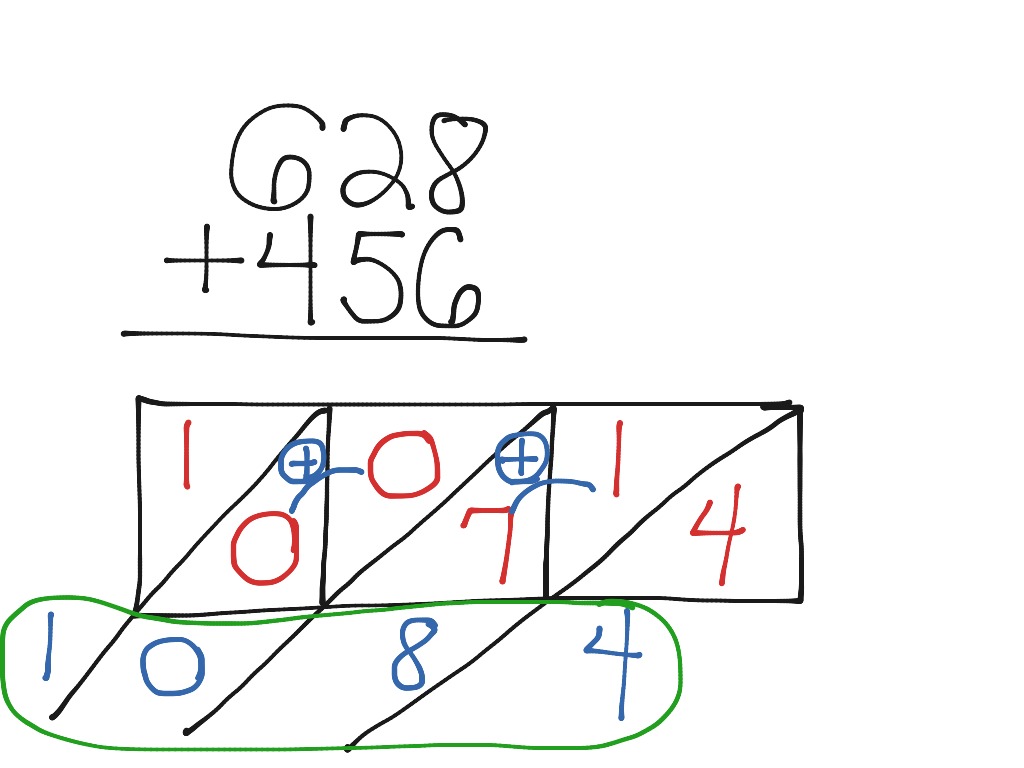 Lattice Algorithm Addition Math Showme
Lattice Algorithm Addition Math Showme
 The Lattice Method Of Addition Science Class 2021 Study Com
The Lattice Method Of Addition Science Class 2021 Study Com
 The Lattice Method Of Addition Science Class 2021 Study Com
The Lattice Method Of Addition Science Class 2021 Study Com
 What Is Lattice Multiplication Knilt
What Is Lattice Multiplication Knilt
 The Lattice Method Of Addition Science Class 2021 Study Com
The Lattice Method Of Addition Science Class 2021 Study Com
 Lattice Method For Multiplication Worksheet Education Com Lattice Method Multiplication Lattice Multiplication
Lattice Method For Multiplication Worksheet Education Com Lattice Method Multiplication Lattice Multiplication
 Lattice Method From Wolfram Mathworld
Lattice Method From Wolfram Mathworld
 The Lattice Method Of Addition Science Class 2021 Study Com
The Lattice Method Of Addition Science Class 2021 Study Com
 The Lattice Method Of Addition Science Class 2021 Study Com
The Lattice Method Of Addition Science Class 2021 Study Com
 The Lattice Discussion Lattice Method Summer Reading Projects Lattice Multiplication
The Lattice Discussion Lattice Method Summer Reading Projects Lattice Multiplication
 Lattice Multiplication Chart Math Methods Upper Elementary Math Classroom Math Activities
Lattice Multiplication Chart Math Methods Upper Elementary Math Classroom Math Activities
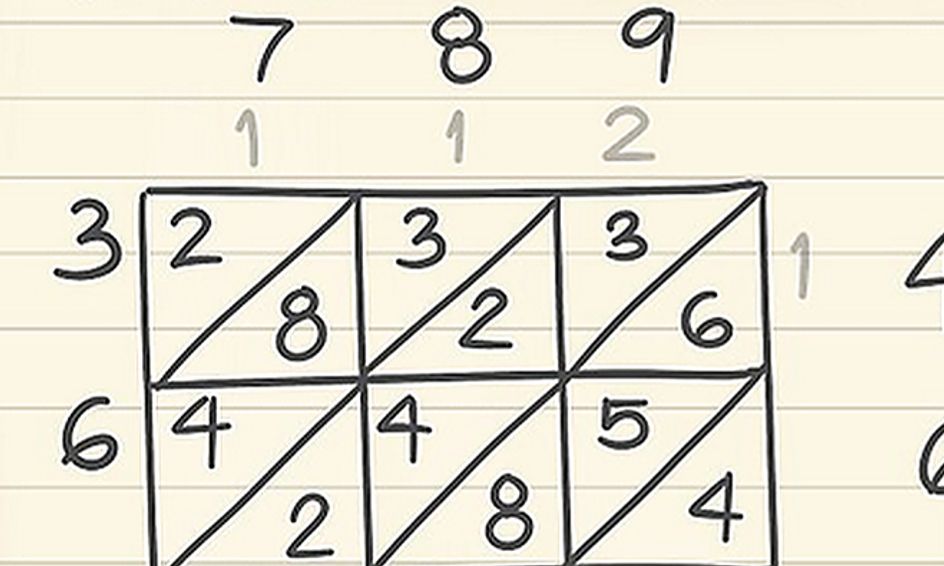
 Pin By Joan Krogman On Multiplication Everyday Math Lattice Multiplication Math Multiplication
Pin By Joan Krogman On Multiplication Everyday Math Lattice Multiplication Math Multiplication